EEG Data Downloads¶
We provide both raw and preprocessed EEG data as a part of the MIPDB dataset.
In order to organize and interpret the EEG data, you will need to click below to download organizational "readme" files that describe the general completion overviews for subjects and explain paradigm coding and operation.
- MIPDB_EEG_Readme - Zip file containing: general Readme file, Readme file for each EEG paradigm, paradigm completion overview sheet, and a Symbol Search key in both excel and .mat format.
- EEG Channel Location File - .sfp file containing the channel location of the EEG montage.
Accessing EEG Data
Public EEG data are distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial Share Alike License. Consistent with the policies of the 1000 Functional Connectomes Project, data usage is unrestricted for non-commercial research purposes. We kindly request that the specific datasets included in analyses be specified appropriately, and that their funding sources be acknowledged.
Each participant’s folder contains one EEG folder, one eye-tracking folder, and one behavioral folder. The data in the EEG folder are available as a simple binary file (.raw) and ascii file (.csv) for each paradigm. There are also two eye-tracker files for each paradigm: one file is segmented into blinks, saccades and fixations (.txt), and the other file is an unsegmented file (.txt), with eye-tracking information for each sample.
Furthermore, a behavioral folder contains a MATLAB file (.mat) for each paradigm, which includes the information about the paradigm itself, including: inter-trial interval, triggers, number of trials, response selection, and reaction time (if available). For users who intend to use the data without MATLAB, this information is also available as .csv files. A “MIPDB_EEG_Readme” folder (linked above) contains “Readme” files for each paradigm about the variables and paradigm parameters.
Data can be accessed one of two ways:
- Clicking in the Direct Downloads section below on individual participants or selecting all participants will start downloads of the selected files.
- Via AWS, accessing the files using Cyberduck, a file transfer program.
Direct Downloads
Subject data is grouped into individual folders (.tar.gz). Each .tar.gz file is approximately 2.5GB in size. Be sure to review Readme files and phenotypic data prior to using this data. Use the checkboxes to select which subjects you would like to download.
- Blue = Male
- Red = Female
AWS and Cyberduck
EEG data, organized into folders by participant, may be accessed through an Amazon Web Services (AWS) S3 bucket.
Each file in the S3 bucket can only be accessed using HTTP (i.e., no ftp or scp ). You can obtain a URL for each desired file and then download it using an HTTP client such as a web browser, wget, or curl. Each file can only be accessed using its literal name- wildcards will not work.
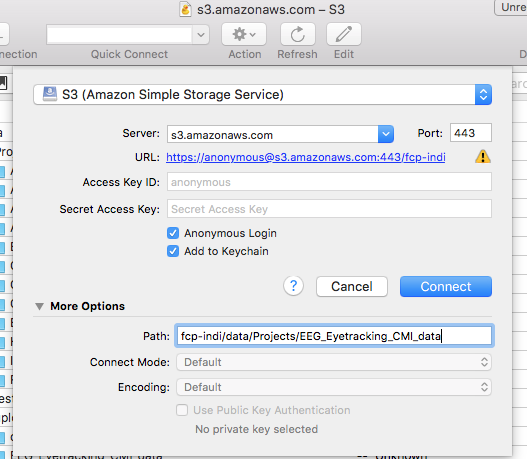
There are file transfer programs that can handle S3 natively and will allow you to navigate through the data using a file browser. Cyberduck is one such program that works with Windows and Mac OS X. Cyberduck also has a command line version that works with Windows, Mac OS X, and Linux. Instructions for using Cyberduck are as follows:
- Open Cyberduck and click on Open Connection.
- Set the application protocol in the dropdown menu to S3 (Amazon Simple Storage Service).
- Set the server to s3.amazonaws.com.
- Check the box labelled Anonymous Login.
- Expand the More Options tab and set Path to fcp-indi/data/Projects/EEG_Eyetracking_CMI_data.
- Click Connect.
The end result should appear as follows: